Thoughts, notes, and explanations on Python, Data Structures, Algorithms, Machine Learning, and learning how to learn effectively.
This section will grow over time with structured posts and practical insights.
Thoughts, notes, and explanations on Python, Data Structures, Algorithms, Machine Learning, and learning how to learn effectively.
This section will grow over time with structured posts and practical insights.

Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) are often treated as a necessary evil, something you grind through only to clear technical interviews. This narrow framing has done more harm than good. It leads to shallow learning, memorized solutions, and frustration when problems slightly change. The truth is simple: DSA is not just about interviews. It is about learning how to think clearly, reason about efficiency, and design solutions that scale. This blog lays out: ...

About This Guide Welcome to the DSA with Python: Zero to Hero comprehensive learning roadmap! This guide serves as the complete reference material for our live course, organizing all topics, concepts, and learning outcomes in a structured, progressive manner. For Course Students If you’re enrolled in the live course, this blog is your companion resource that: Mirrors the course structure - Every module taught in class is documented here Serves as a reference - Quickly look up concepts, syntax, and examples Tracks your progress - Follow along and check off completed modules Provides continuity - Never miss a beat even if you miss a session For Self-Learners Even if you’re not enrolled in the course, this roadmap is designed to be: ...
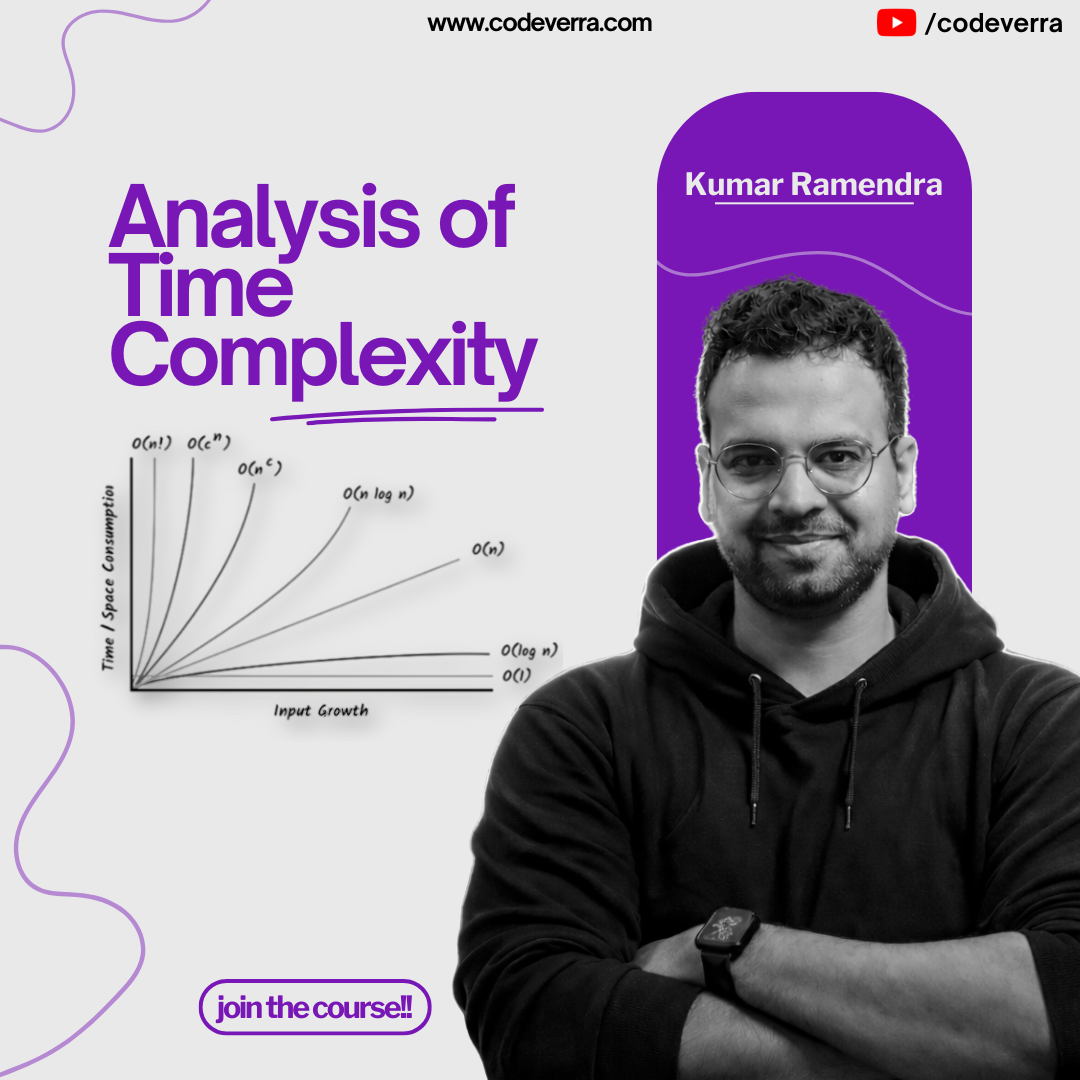
Time complexity is one of the most important concepts in Data Structures and Algorithms. It helps you understand how an algorithm behaves as the input size grows and why some solutions fail to scale. This guide explains time complexity step-by-step using simple explanations and Python examples written purely as text, focusing on intuition rather than heavy mathematics. 1. What Is Time Complexity? Time complexity measures how the running time of an algorithm grows as the input size increases. ...

Array patterns are recurring problem-solving techniques used to solve a wide variety of array problems efficiently. Instead of memorizing individual solutions, understanding these patterns helps you recognize how to approach a problem and design an optimal solution. 1. Traversal Pattern Concept The traversal pattern involves visiting each element of the array once or in a fixed manner. When to Use Finding maximum or minimum elements Printing all elements Counting frequency Simple condition checks Explanation Example Traverse the array from the first element to the last, updating the required result as you move forward. ...

Graphs and trees are non-linear data structures. To process or explore them, traversal algorithms are used. The two most important traversal techniques are: Breadth-First Search (BFS) Depth-First Search (DFS) Both algorithms visit all nodes in a graph or tree, but their strategies and use-cases differ significantly. 1. Breadth-First Search (BFS) Concept Breadth-First Search explores a graph level by level. It visits all neighbors of a node before moving deeper into the graph. ...

Binary Search is an efficient searching algorithm used to find an element in a sorted array by repeatedly dividing the search space into half. Unlike linear search, which checks elements one by one, binary search eliminates half of the remaining elements at each step. This makes it significantly faster for large datasets. Key Requirement Binary search can only be applied when the array is already sorted. The sorting order can be: ...

Python is one of the most versatile and beginner-friendly programming languages in the world. From web development and automation to data science and AI, Python forms the backbone of modern software development. This syllabus is designed as a structured learning roadmap, not just a list of topics. It focuses on building strong fundamentals, clear thinking, and professional-level coding skills. This guide covers: Python fundamentals from scratch Core programming concepts Advanced Python features Career-oriented applications Interview and professional preparation Beginner Level — Python Foundations 1. Introduction to Python What is Python History and features of Python Applications of Python Python vs other languages Installing Python Python versions Running Python programs Python interactive shell Writing your first Python program 2. Python Basics & Syntax Python keywords Identifiers Indentation and code structure Comments (single-line and multi-line) Variables and naming conventions Data types overview Type checking using type() Type conversion 3. Input, Output & Operators Input using input() Output using print() Formatted output Arithmetic operators Relational operators Logical operators Assignment operators Operator precedence 4. Control Flow Conditional Statements if if-else elif Nested conditions Looping Statements for loop while loop Loop Control break continue pass Intermediate Level — Core Python Concepts 5. Strings String creation Indexing and slicing String methods String formatting Escape characters Immutability String operations 6. Lists Creating lists Indexing and slicing List methods Nested lists Iterating through lists List comprehensions 7. Tuples Creating tuples Tuple operations Tuple unpacking Difference between list and tuple Use cases 8. Sets Set creation Set methods Set operations Difference between set and list Use cases 9. Dictionaries Dictionary creation Accessing elements Dictionary methods Iterating dictionaries Nested dictionaries Real-world use cases 10. Functions Defining functions Function parameters Return values Default arguments Keyword arguments Variable-length arguments (*args, **kwargs) Scope (local and global) Lambda functions 11. Modules & Packages Importing modules Built-in modules Creating custom modules Python packages __name__ == "__main__" Virtual environments Advanced Level — Professional Python 12. File Handling Reading files Writing files File modes Working with CSV files JSON handling Context managers using with 13. Exception Handling Types of errors try and except else and finally Multiple exceptions Custom exceptions Debugging techniques 14. Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Classes and objects Constructors Instance and class variables Methods Encapsulation Inheritance Polymorphism Abstraction Magic methods (__str__, __len__, etc.) 15. Advanced Python Concepts List, set, and dictionary comprehensions Iterators and generators Decorators Closures Shallow vs deep copy Memory management Garbage collection 16. Python Standard Library math random datetime collections itertools functools os sys 17. Testing & Debugging Assertions Unit testing Writing test cases Testing frameworks overview Debugging tools Logging Specialized & Career-Oriented Topics 18. Data Structures & Algorithms with Python Time and space complexity Arrays and strings Stacks and queues Linked lists Trees Graphs Dynamic programming Greedy algorithms Recursion and backtracking 19. Automation & Scripting File and folder automation Web scraping basics Task scheduling Command-line tools Automation projects 20. Python for Web Development Backend fundamentals REST APIs JSON and HTTP Web frameworks overview Request–response cycle 21. Python for Data & AI NumPy basics Pandas basics Data cleaning Basic data visualization Working with datasets 22. Performance & Optimization Code optimization Profiling Efficient data handling Best practices PEP 8 guidelines Type hints 23. Real-World Projects Beginner mini projects Automation projects API-based projects Data-driven projects End-to-end Python applications 24. Interview & Professional Topics Common Python interview questions DSA problem solving Design patterns Code optimization Packaging and distribution Resume and project preparation 25. Python Programming Playlist --- More structured Python learning guides and hands-on roadmaps coming soon.

Dynamic Programming (DP) is a powerful algorithmic technique used to solve problems that can be broken down into smaller subproblems whose solutions are reused to efficiently compute the final result. Unlike brute-force approaches or naive recursion, Dynamic Programming avoids unnecessary recomputation and significantly improves performance. 1. What Is Dynamic Programming? Dynamic Programming is a method of solving problems by: Dividing a problem into smaller subproblems Solving each subproblem only once Storing the solution of each subproblem Using stored solutions to build the final answer The word dynamic refers to solving problems step by step, while programming refers to structured problem-solving rather than coding. ...

Sorting is the process of arranging elements in a specific order, usually ascending or descending, to make data easier to search, analyze, and process. Sorting plays a critical role in computer science because many algorithms perform efficiently only on sorted data. 1. Bubble Sort Concept Bubble Sort repeatedly compares adjacent elements and swaps them if they are in the wrong order. Larger elements gradually move to the end of the array, similar to bubbles rising to the surface. ...

Recursion is a programming technique in which a function calls itself to solve a problem by breaking it down into smaller and simpler subproblems. Instead of solving the entire problem at once, recursion focuses on solving a reduced version of the problem repeatedly until a stopping condition is reached. What Is Recursion? In recursion, a function solves a problem by calling itself with a smaller input. Each recursive call works on a reduced version of the original problem until it reaches a point where no further calls are needed. ...